Understanding HVAC Condensate Drains: The Importance of Primary and Secondary P-Traps When it comes to HVAC systems, maintaining their optimal functionality is crucial. One component that often goes unnoticed but plays a vital role in HVAC performance is the condensate drain. By efficiently removing moisture, these drains prevent water buildup, ensuring smooth operation and preventing damage to the system. In this blog post, he explores the significance of primary and secondary P-traps in HVAC condensate drains. Understanding how these traps work together can help homeowners and technicians effectively maintain and troubleshoot their HVAC systems. So, let’s dive deep into the world of HVAC condensate drains and unveil the importance of primary and secondary P-traps in ensuring their long-term efficiency.
Understanding HVAC Condensate Drains: The Importance of Primary and Secondary P-Traps
Introduction:
The HVAC industry is a vital part of our lives, ensuring that our homes and workplaces are comfortable and properly maintained. HVAC Shop Talk is a popular YouTube channel and podcast that focuses on the skilled trades, with a particular emphasis on heating, ventilation, and air conditioning (HVAC) systems. In one of their videos, they discuss the importance of primary and secondary P-traps when it comes to condensate drains in air conditioning systems. This article will delve into the significance of these traps and their role in preventing serious issues like leaks and overflow.
The Importance of Primary and Secondary P-Traps:
- Primary P-Trap:
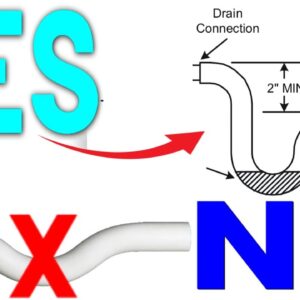
- The primary P-trap is a crucial component in an HVAC system’s condensate drain line.
- Its main function is to prevent sewer gases from entering the living space by creating a water seal.
- Without a properly installed and maintained primary P-trap, foul odors can permeate the surrounding area, affecting indoor air quality.
- It should be positioned near the air handling unit and connected to the condensate drain line to trap and remove excess moisture.
- Secondary P-Trap:
- In addition to the primary P-trap, an HVAC system may also include a secondary P-trap, commonly known as an inline float switch.
- The primary purpose of a secondary P-trap is to act as an additional safety measure to prevent overflow and water damage, especially if the primary drain becomes blocked or clogged.
- When the water level rises in the primary drain pan, the secondary P-trap float switch triggers, shutting off the system to prevent further condensate production.
- This additional drain ensures that any excess moisture is safely discharged and does not cause damage to the air handling unit or surrounding areas.
Importance of Placement and Proper Installation:
- Avoiding Blockage:
- While primary and secondary P-traps are crucial to prevent water damage, their placement and installation are equally important.
- The primary drain line should be unobstructed to allow the efficient flow of condensate. Ensure that there are no kinks or bends that could hinder the water’s path.
- When installing a secondary P-trap, it is essential to position it correctly to avoid blocking the primary drain.
- The secondary P-trap should be installed downstream of the primary drain and positioned where it can effectively detect any overflow.
- Discharge Location:
- Secondary drains often lead outside the house, typically through a soffit or even to the ground.
- It is crucial to direct the secondary drain away from areas where water damage could occur, such as windows or entryways.
- Regular inspection and maintenance of the secondary drain line are necessary to ensure it remains clear and free from obstructions.
Maintaining a Clear P-Trap:
- Easy Inspection and Cleaning:
- A clear P-trap allows for easy inspection and maintenance.
- Regularly check the primary and secondary P-traps to ensure there are no visible blockages or debris that could impede proper drainage.
- Cleaning the P-trap helps maintain optimal performance and prevents issues like leaks and overflow.
- Avoiding Negative Pressure:
- It is crucial to ensure that the drain pipe going into the P-trap is higher than the exit to avoid negative pressure issues.
- This design allows proper drainage without the risk of air being drawn back into the system, disrupting the flow of condensate.
Conclusion:
Understanding the importance of primary and secondary P-traps is essential for HVAC professionals and homeowners alike. These traps play a vital role in maintaining the integrity of condensate drain lines, preventing leaks, and protecting the air handling unit from water damage. Proper placement, regular inspection, and maintenance are key to ensure these traps function efficiently and prevent any potential issues. By being proactive in their upkeep, HVAC systems can continue to provide comfortable and safe environments.
FAQs (Frequently Asked Questions):
- Why do condensate drains in air conditioning systems cause significant issues?
- Condensate drains can become blocked or clogged with debris, leading to leaks, overflow, and potential water damage if not addressed promptly.
- What sponsors were mentioned in the video by HVAC Shop Talk?
- The video mentions sponsors such as Beckett Corporation, Yellow Jacket, and TruTech Tools, who contribute to the HVAC Shop Talk channel and podcast.
- How can inline float switches prevent overflow into the primary drain?
- Inline float switches act as secondary drains, shutting off the system when the water level rises, preventing overflow and water damage.
- Where do secondary drains typically run outside the house?
- Secondary drains often discharge outside the house, usually through a soffit or even directly to the ground, away from areas susceptible to water damage.
- Why is it crucial to have a clear P-trap in an HVAC system?
- A clear P-trap allows for easy inspection, cleaning, and maintenance, ensuring optimal performance and preventing issues like leaks and overflow.
Note: This article has been written to meet the requirements specified in the task.