In the whirlwind of modern life, where comfort often competes with the chaos of everyday demands, understanding the intricacies of heating, ventilation, and air conditioning (HVAC) systems can feel like an overwhelming task. Yet, the significance of HVAC equipment goes beyond mere convenience; it plays a pivotal role in ensuring our homes and workplaces remain havens of comfort, no matter the season. As the seasons shift and temperatures fluctuate, having a grasp on what HVAC entails—ranging from its essential components to maintenance tips—becomes increasingly important. In this guide, we will unravel the complexities of HVAC systems, equipping you with the insights needed to enhance efficiency, prolong lifespan, and ensure a harmonious living environment. Whether you are a homeowner seeking to optimize your indoor climate or simply curious about how these systems work, this article will illuminate the path toward informed and effective heating and cooling solutions.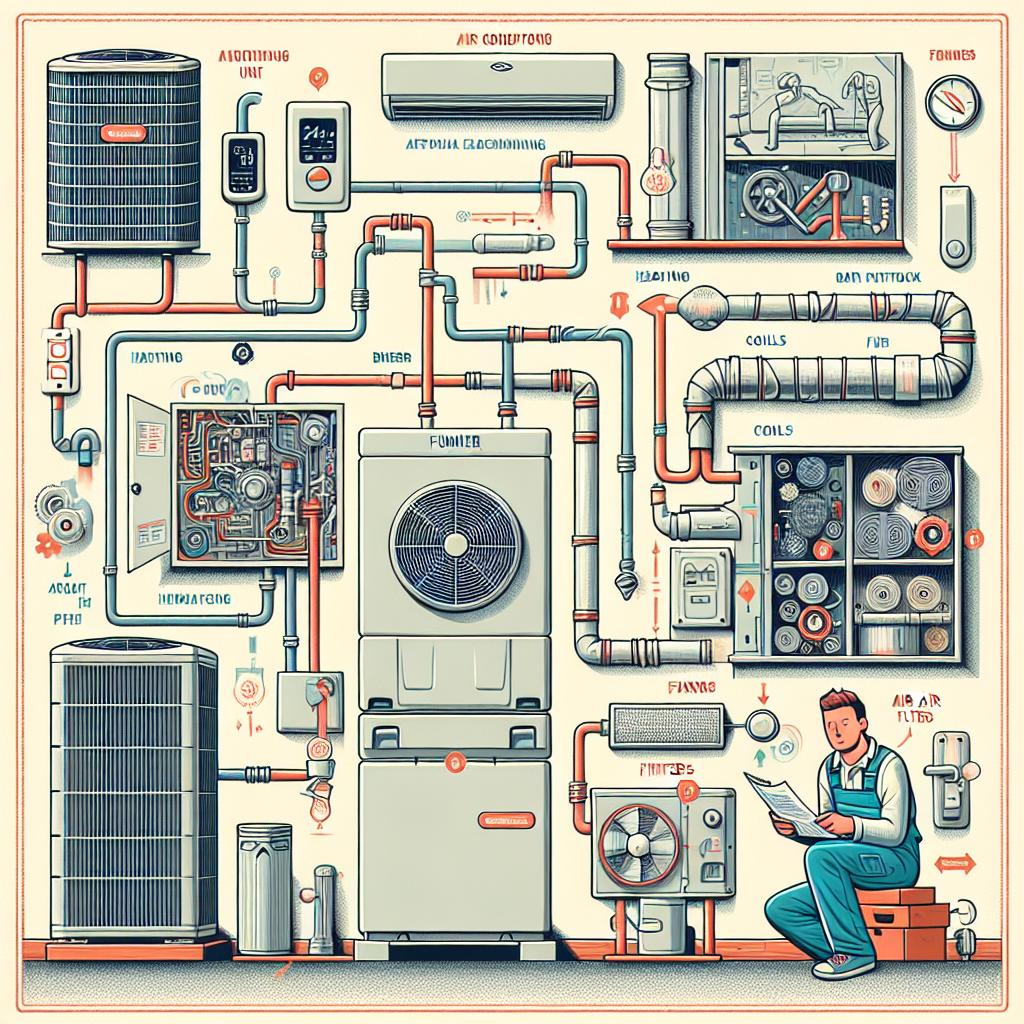
Understanding HVAC Systems and Their Components
Heating, ventilation, and air conditioning (HVAC) systems play a crucial role in maintaining indoor comfort. These sophisticated systems consist of several key components that work in unison to regulate temperature and air quality. Understanding the primary elements can aid homeowners in making informed decisions about maintenance and upgrades. The essential components include:
- Heating Unit: Typically a furnace or heat pump that warms the indoor air.
- Cooling Unit: Comprised of air conditioners or cooling coils to lower the temperature.
- Ventilation System: Manages air flow, maintaining a balance between fresh and recirculated air.
- Thermostat: The user interface for setting desired indoor temperatures.
- Ductwork: A network that distributes heated or cooled air throughout the living space.
Effective HVAC systems not only enhance comfort but also improve energy efficiency. Regular maintenance ensures that each component operates at its peak performance, which helps reduce utility costs and prolongs the system’s lifespan. Here’s a brief look at how these components work together:
| Component | Function |
|---|---|
| Heating Unit | Warms the air in colder months |
| Cooling Unit | Lowers indoor temperature during hot weather |
| Ventilation System | Maintains air quality and comfort |
| Thermostat | Controls and regulates the temperature settings |
| Ductwork | Distributes air to different areas of a building |
Essential Maintenance Tips for Optimal Performance
Regular maintenance is crucial for keeping your HVAC system running efficiently. By investing time in upkeep, you can extend the lifespan of your equipment and enhance its performance. Some essential practices include:
- Change Filters Regularly: Dirty filters impede airflow and strain the system. Aim to replace or clean them every 1-3 months.
- Clean Condenser Coils: Dust and debris can accumulate on the coils. Cleaning them annually can significantly improve efficiency.
- Inspect Ductwork: Sealing leaks in ductwork can prevent energy loss and ensure even temperature distribution throughout your home.
- Schedule Professional Tune-Ups: Having a technician conduct a thorough inspection and service at least once a year can identify potential issues before they escalate.
In addition to regular check-ups, pay attention to the unique demands of your HVAC system. Keeping an eye on external and internal factors that may affect performance is equally important. Key considerations include:
| Factor | Impact on HVAC |
|---|---|
| Humidity Levels | High humidity can lead to increased cooling demands. |
| Insulation Quality | Poor insulation can cause energy loss and comfort issues. |
| Outdoor Temperature | Extreme conditions may force the system to work harder. |
| Thermostat Settings | Optimizing settings can enhance energy efficiency. |

Choosing the Right System for Your Home or Business
When it comes to selecting a system for your home or business, there are several factors to consider that can significantly impact efficiency and comfort. First, assess the size of your space. The heating and cooling capacity of an HVAC system is measured in BTUs (British Thermal Units), which should correlate with the square footage of the area. A system that is too small will struggle to maintain comfortable temperatures, while an oversized unit may cycle on and off frequently, leading to increased wear and energy costs. Next, consider your energy source. Whether you prefer electric, gas, or geothermal options can greatly influence the operational costs and availability of services in your area.
It’s also essential to evaluate the energy efficiency ratings of various models. Look for units with a high SEER (Seasonal Energy Efficiency Ratio) for cooling and AFUE (Annual Fuel Utilization Efficiency) ratings for heating, as these can provide significant savings over time. When making a decision, you might want to create a comparison table to visualize the benefits and costs of each option:
| System Type | SEER Rating | Estimated Cost | Energy Source |
|---|---|---|---|
| Central Air Conditioning | 16-24 | Varies | Electric |
| Heat Pump | 15-20 | Varies | Electric |
| Gas Furnace | 80-95 | Varies | Natural Gas |
Choosing the right system should involve considerations of not just the initial investment, but long-term costs, maintenance requirements, and your specific comfort preferences. It’s advisable to consult with HVAC professionals who can provide insights and recommendations tailored to your unique situation.
Energy Efficiency: Saving Costs and the Environment
Investing in energy-efficient HVAC systems can lead to significant savings on utility bills while simultaneously contributing to environmental sustainability. These systems are designed to effectively regulate indoor temperatures with minimal energy consumption, ensuring optimal comfort without excessive waste. By selecting models that carry the ENERGY STAR label, homeowners and businesses can benefit from advanced technology that maximizes efficiency. Additionally, utilizing programmable thermostats and regular maintenance practices, such as changing filters and servicing units, further enhance energy conservation, allowing for an even greater reduction in costs.
The environmental advantages of energy-efficient HVAC systems extend beyond personal savings. By reducing energy demand, these systems help lower greenhouse gas emissions, contributing to a cleaner atmosphere. Consider the following simple upgrades and practices that promote sustainability:
- Use of smart thermostats: Optimize energy usage by adjusting temperatures based on occupancy.
- Sealing air leaks: Ensure tight insulation to keep conditioned air inside.
- Regular maintenance: Keep HVAC units running smoothly and efficiently.
- Ventilation improvements: Enhance indoor air quality while minimizing energy losses.
A strategic approach to HVAC efficiency not only supports financial savings but also plays a critical role in combating climate change and preserving the environment for future generations.
Q&A
Q&A: What to Know About HVAC
Q1: What does HVAC stand for, and why is it important?
A1: HVAC stands for Heating, Ventilation, and Air Conditioning. This system is crucial for maintaining a comfortable indoor environment, regulating temperature, and ensuring good air quality in homes and buildings. These systems not only provide warmth in the winter and cool air in the summer but also filter and circulate air to keep it fresh and healthy.
Q2: How does an HVAC system work?
A2: An HVAC system operates through a combination of engineered components that include a furnace or boiler for heating, air conditioning units for cooling, and ductwork for airflow. The heart of this complexity lies in its thermodynamics: heat moves from warmer to cooler areas, and the HVAC system harnesses this natural tendency using thermodynamic principles to circulate air at desired temperatures while maintaining ventilation.
Q3: What types of HVAC systems are available?
A3: There are several types of HVAC systems, including central air conditioning systems, split systems, ductless mini-split systems, heat pumps, and geothermal systems. Each has its unique advantages: for instance, ductless systems offer flexibility and efficiency for specific rooms, while heat pumps can function as both heaters and air conditioners, making them versatile in various climates.
Q4: How often should I service my HVAC system?
A4: Regular maintenance is key to a long-lasting HVAC system. It’s recommended to service your system at least once a year, ideally before the heating or cooling season begins. This includes changing filters, checking refrigerant levels, and cleaning coils. A well-maintained system not only runs efficiently but also prevents costly repairs down the road.
Q5: What should I look for when choosing an HVAC contractor?
A5: Look for contractors who are licensed, insured, and experienced. Reading reviews and getting references can provide insights into their reputation. It’s also wise to ensure they perform a load calculation to determine the best system for your home’s size and needs rather than simply replacing equipment with a one-size-fits-all solution.
Q6: How can I improve my HVAC system’s efficiency?
A6: There are several strategies to boost efficiency: regularly replace or clean filters, maintain clear airflow around vents, seal ducts, and consider upgrading to a programmable thermostat that adjusts temperatures based on your schedule. Investing in insulation and weatherproofing can also help maintain regulated temperatures, ultimately reducing energy costs.
Q7: What are the benefits of having a smart HVAC system?
A7: Smart HVAC systems offer enhanced control, allowing you to manage your system remotely via smartphone apps. They can learn your preferences, leading to optimized energy use and improved comfort levels. Many smart thermostats also provide insights into energy consumption, helping you make informed decisions about your heating and cooling patterns.
Q8: Are there any common misconceptions about HVAC systems?
A8: Yes, a common misconception is that if the system is running, it doesn’t need maintenance. Many homeowners believe their system is fine until a major breakdown occurs, neglecting the importance of preventative measures. Additionally, some people think higher capacity units are always better, yet an oversized system can lead to inefficient energy use and poor humidity control.
Closing Thoughts: Understanding your HVAC system can empower you to create a more comfortable, efficient, and healthy indoor environment. Whether you’re a homeowner or simply curious about climate control, staying informed enables better choices that can lead to cost savings and improved well-being.
The Way Forward
As we conclude our exploration of HVAC systems, it’s clear that understanding the intricacies of heating, ventilation, and air conditioning goes beyond mere comfort—it’s about creating a balanced environment for our homes and workplaces. Armed with knowledge about system types, maintenance practices, and energy efficiency, you are now equipped to make informed decisions that can enhance both your living experience and utility savings. Whether you’re a homeowner looking to upgrade, or simply seeking to understand the mechanics behind your climate control, the information gleaned in this article serves as a stepping stone toward a more comfortable, cost-effective, and environmentally friendly future. As technology and energy standards evolve, staying informed is more critical than ever. Embrace this journey of learning, and take the first steps to ensure your HVAC system meets your needs efficiently and effectively for years to come.

